Hi, my fellow malware enthusiast,
Had my first fight last week, and guess what? I won! It was a good experience. Winning made all of the sacrifices worth it! Shoutout to my opponent; he gave a good fight! I’m just glad I can finally eat what I want. Honestly, the diet and the preparation were harder than the fight. I’m looking forward to getting back on my malware research; I had to take a break and focus entirely on my fight. Enjoy this week's newsletter, and see you on the next one!
📰In today’s newsletter
A New Threat to Air-Gapped Systems
GeoServer Flaw Sparks Global Hacking Campaigns
SonicWall SSL-VPN Access Control Flaw Under Attack
Inside FIN7’s Latest Stealth Tool
BlindEagle Targets Colombian Insurance Sector with BlotchyQuasar Malware
Android Malware Steals Crypto Credentials with Image Recognition
Fog Ransomware Targets Financial Sector with Precision
Fake OnlyFans Tool Steals Cybercriminals' Passwords
Hundreds of Online Stores Compromised in New Cyber Campaign
PenPie DeFi Protocol Hit by $1 Million Theft in Ethereum Attack
A New Threat to Air-Gapped Systems
A new type of cyberattack called "Rambo" has emerged, targeting air-gapped computers—those not connected to the internet. This attack stands out by using the computer's RAM (random access memory) to steal data without leaving a trace. Developed by researchers, the Rambo attack reads electromagnetic signals emitted from RAM operations, allowing attackers to capture sensitive information from even the most isolated systems. The technique bypasses traditional security measures by using specialized equipment to interpret these signals, effectively making what was thought to be a secure environment vulnerable.
For cybersecurity professionals, this attack underlines the evolving risks to critical infrastructure, where air-gapped systems are common. It highlights the need for new defense strategies that go beyond conventional network security, particularly for protecting high-value targets like government and military data. As this research shows, no system is truly off-limits to determined attackers.
🔗Link
GeoServer Flaw Sparks Global Hacking Campaigns

A critical vulnerability has been identified in GeoServer, a popular open-source platform used for sharing geospatial data. This flaw, which enables remote code execution, is being actively exploited by hackers in global campaigns. Attackers can exploit the vulnerability to take control of servers, manipulate data, and potentially disrupt services that rely on geospatial information, including government and environmental monitoring systems. The vulnerability is particularly concerning because GeoServer is widely used, making it an attractive target for cybercriminals.
For those managing GeoServer deployments, it’s crucial to update systems immediately to mitigate the risk of exploitation. This flaw serves as a stark reminder of the importance of regular patching and the potential widespread impacts of unpatched vulnerabilities in commonly used open-source software.
🔗Link
SonicWall SSL-VPN Access Control Flaw Under Attack

Cybercriminals are now exploiting a newly discovered access control vulnerability in SonicWall SSL-VPN appliances, which are widely used by organizations to secure remote connections. This flaw allows attackers to bypass authentication measures, giving them unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems. Exploiting this vulnerability can lead to significant breaches, especially in environments where these devices serve as critical gateways to corporate networks.
Security experts are urging organizations using SonicWall SSL-VPN appliances to apply the latest patches immediately to protect against these attacks. The active exploitation of this flaw highlights the increasing risks associated with outdated or unpatched security devices and underscores the need for vigilant patch management practices to safeguard against evolving threats.
🔗Link
Inside FIN7’s Latest Stealth Tool
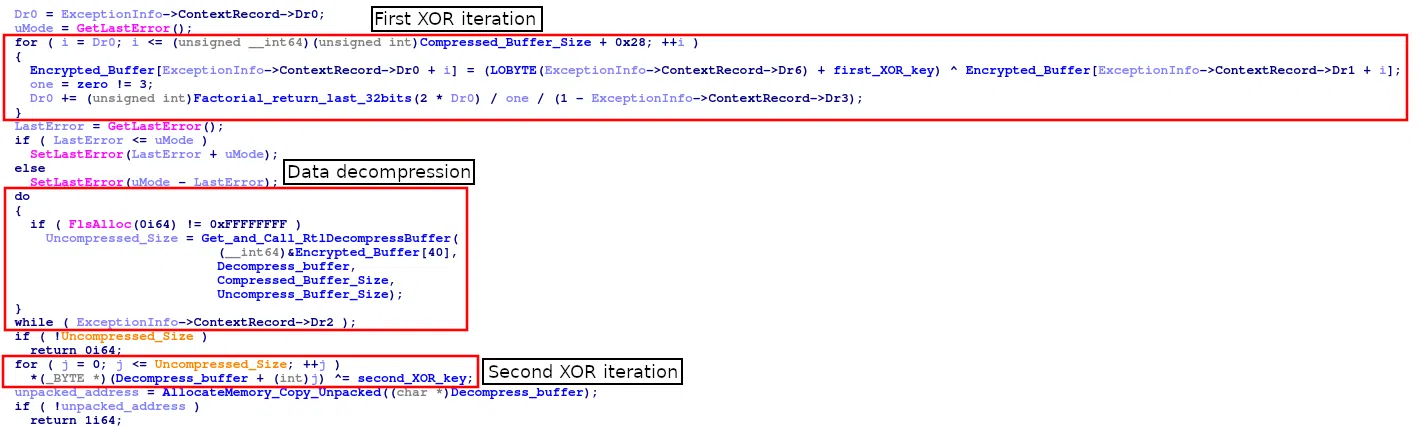
Researchers have exposed a new packer called PackXor, used by the notorious cybercrime group FIN7 to evade detection during their malicious campaigns. A packer is a tool that compresses or encrypts malware to make it harder for security software to detect. PackXor stands out for its use of complex techniques, including unique encryption methods that conceal malware payloads from standard security scans, making it particularly challenging to identify and analyze.
The discovery of PackXor offers valuable insights into FIN7’s evolving tactics, demonstrating their ongoing commitment to creating sophisticated tools that bypass even advanced defenses.
🔗Link
BlindEagle Targets Colombian Insurance Sector with BlotchyQuasar Malware

The threat actor BlindEagle has launched a targeted attack against the Colombian insurance sector using BlotchyQuasar, a sophisticated malware strain with advanced capabilities. BlotchyQuasar spreads through phishing emails that contain malicious attachments, often disguised as legitimate documents relevant to the industry. Once opened, the malware exploits vulnerabilities in the victim’s system to establish a foothold. BlotchyQuasar is equipped with various modules, including a keylogger, screen capture tool, and data exfiltration capabilities, allowing attackers to collect sensitive information such as personal identifiers, financial records, and internal communications.
Technically, BlotchyQuasar uses a combination of obfuscation techniques and command-and-control (C2) communication to evade detection. It employs a customized encryption method to disguise its payloads and uses multiple stages of execution to avoid triggering traditional antivirus solutions. The malware also uses a modular architecture, which allows attackers to easily add new functionalities or adapt the malware for different targets. For cybersecurity professionals, this attack emphasizes the need for advanced threat detection solutions that can identify such multi-stage, obfuscated threats before they cause significant damage.
🔗Link
Android Malware Steals Crypto Credentials with Image Recognition
A new Android malware campaign, known as SpyAgent, is actively targeting cryptocurrency users by stealing their credentials using an innovative image recognition technique. This malware disguises itself as a legitimate app, luring users to download it from unofficial sources. Once installed, SpyAgent gains extensive permissions, allowing it to monitor the device, capture screen activity, and access sensitive information.
Technically, SpyAgent uses Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to extract credentials from images displayed on the device’s screen, such as screenshots of crypto wallets or exchange apps. This method bypasses traditional input-based security measures like keyboard encryption. Additionally, SpyAgent communicates with its command-and-control (C2) server to transmit stolen data, making it difficult for victims to realize their credentials have been compromised. To protect against such threats, users should stick to official app stores, carefully scrutinize app permissions, and employ robust mobile security solutions capable of detecting these advanced attack techniques.
🔗Link
Fog Ransomware Targets Financial Sector with Precision

The newly identified Fog ransomware is actively targeting the financial sector, deploying sophisticated tactics to lock critical data and demand ransom payments. Fog ransomware distinguishes itself by using advanced evasion techniques, such as encrypting its payloads to avoid detection by traditional antivirus solutions and employing a multi-stage infection process. This process begins with phishing emails that deliver malicious attachments or links, which, when accessed, initiate the download of the ransomware onto the victim's network.
Fog ransomware encrypts files using a robust encryption algorithm, rendering them inaccessible without the decryption key, which the attackers offer in exchange for a ransom. It also disables system restore points and backups, making recovery without paying the ransom particularly challenging. Additionally, the ransomware is capable of spreading laterally within a network, compromising multiple devices and amplifying its impact.
🔗Link
Fake OnlyFans Tool Steals Cybercriminals' Passwords

A clever new trap is turning the tables on cybercriminals by luring them with a fake hacking tool designed to exploit OnlyFans accounts. This tool, which promises to help hackers gain unauthorized access to OnlyFans content, is actually a trojan that steals credentials from those who attempt to use it. Once installed, the fake tool captures sensitive information, including passwords and other login details from the would-be hackers, and sends this data back to the tool’s creators.
Technically, the trojan operates by masquerading as a legitimate executable but includes hidden malicious code that activates upon launch. It uses common credential-stealing methods such as keylogging and intercepting data from web browsers, targeting a variety of platforms and services used by the attacker. This unique approach not only disrupts the activities of cybercriminals but also highlights a creative method of using their own tactics against them.
🔗Link
Hundreds of Online Stores Compromised in New Cyber Campaign

A recent cyber campaign has resulted in the compromise of hundreds of online stores, impacting a wide range of e-commerce platforms. Attackers are using a sophisticated technique involving malicious code injections to exploit vulnerabilities in the stores' software. This attack primarily targets e-commerce sites by injecting malicious scripts into their web pages, which then capture sensitive customer information, such as credit card details and personal data, as users make purchases.
The attackers exploit weaknesses in the web applications and inject JavaScript or other types of malicious code into the stores' payment processing systems. This code runs silently in the background, intercepting payment information before it is securely transmitted to the payment gateway.
🔗Link
PenPie DeFi Protocol Hit by $1 Million Theft in Ethereum Attack

The PenPie decentralized finance (DeFi) protocol has been struck by a significant security breach, resulting in the theft of approximately $1 million in Ethereum. The attack exploited a vulnerability in the protocol’s smart contracts, which are used to facilitate and manage financial transactions within the DeFi ecosystem.
Technically, the attackers manipulated the smart contract’s code to siphon off funds from the protocol's liquidity pool. This exploit involved crafting a malicious transaction that tricked the contract into allowing unauthorized withdrawals. The attack underscores the risks associated with smart contract vulnerabilities and highlights the need for rigorous security audits and testing before deploying DeFi protocols.
🔗Link
✉️ Wrapping Up
In the world of malware, understanding is key. As we delve into these threats together, remember that knowledge and vigilance are our best allies.
If you find this newsletter helpful and know others who might benefit from it, I'd be grateful if you could pass it along. 🙏
Until next time, stay informed and keep your defenses sharp. Here’s to staying one step ahead
Thanks for reading!